Plugin System
The plugin system allows you to extend Location's functionality by adding various plugins, supporting scenarios like authentication, flow control, response header settings, etc. Through plugins, you can flexibly customize the request handling process.
Plugin Execution Points
Plugins can execute at different stages of request processing, currently supporting three timing points:
-
Request: At the very beginning of the request- Suitable for early interception scenarios like permission verification
-
ProxyUpstream: Before forwarding to upstream nodes- Executes after reading from cache
- Suitable for scenarios that need to limit upstream access but allow cache access
- Example: Limiting request rate to upstream while allowing high concurrency cache reads
-
Response: After upstream response- Used for processing and modifying response data from upstream
#[async_trait]
pub trait Plugin: Sync + Send {
/// Returns a unique key that identifies this specific plugin instance.
///
/// # Purpose
/// - Can be used for caching plugin results
/// - Helps differentiate between multiple instances of the same plugin type
/// - Useful for tracking and debugging
///
/// # Default
/// Returns an empty string by default, which means no specific instance identification.
fn hash_key(&self) -> String {
"".to_string()
}
/// Processes an HTTP request at a specified lifecycle step.
///
/// # Parameters
/// * `_step` - Current processing step in the request lifecycle (e.g., pre-routing, post-routing)
/// * `_session` - Mutable reference to the HTTP session containing request data
/// * `_ctx` - Mutable reference to the request context for storing state
///
/// # Returns
/// * `Ok((executed, response))` where:
/// * `executed` - Boolean flag:
/// - `true`: Plugin performed meaningful logic for this request
/// - `false`: Plugin was skipped or did nothing for this request
/// * `response` - Optional HTTP response:
/// - `Some(response)`: Terminates request processing and returns this response to client
/// - `None`: Allows request to continue to next plugin or upstream
/// * `Err` - Returns error if plugin processing failed
///
/// # Example
/// ```
/// // A plugin that blocks requests with a specific User-Agent
/// async fn handle_request(&self, _step, session, _ctx) -> Result<(bool, Option<HttpResponse>)> {
/// let user_agent = session.get_header_str("User-Agent");
/// if user_agent.contains("BadBot") {
/// // Block the request with 403 Forbidden
/// let resp = HttpResponse::new(StatusCode::FORBIDDEN);
/// return Ok((true, Some(resp)));
/// }
/// // Allow the request to proceed
/// Ok((true, None))
/// }
/// ```
async fn handle_request(
&self,
_step: PluginStep,
_session: &mut Session,
_ctx: &mut Ctx,
) -> pingora::Result<(bool, Option<HttpResponse>)> {
Ok((false, None))
}
/// Processes an HTTP response at a specified lifecycle step.
///
/// # Parameters
/// * `_step` - Current processing step in the response lifecycle
/// * `_session` - Mutable reference to the HTTP session
/// * `_ctx` - Mutable reference to the request context
/// * `_upstream_response` - Mutable reference to the upstream response header
///
/// # Returns
/// * `Ok(modified)` - Boolean flag:
/// - `true`: Plugin modified the response in some way
/// - `false`: Plugin did not modify the response
/// * `Err` - Returns error if plugin processing failed
///
/// # Example
/// ```
/// // A plugin that adds a custom header to all responses
/// async fn handle_response(&self, _step, _session, _ctx, upstream_response) -> Result<bool> {
/// upstream_response.insert_header("X-Served-By", "My-Proxy-Service");
/// Ok(true) // Indicate that we modified the response
/// }
/// ```
async fn handle_response(
&self,
_step: PluginStep,
_session: &mut Session,
_ctx: &mut Ctx,
_upstream_response: &mut ResponseHeader,
) -> pingora::Result<bool> {
Ok(false)
}
}
There are three main implementations:
category: Plugin type, used to distinguish what form of plugin it isstep: Plugin execution timing, choose timing based on needs, different plugins have different choiceshandle_request: Plugin's pre-forwarding execution logic. If returnsOk((true, Some(HttpResponse))), indicates request is complete, won't forward to upstream, and will transmit response to clienthandle_response: Plugin's pre-response execution logic. If returnsOk(bool), that means the plugin is executed successful.
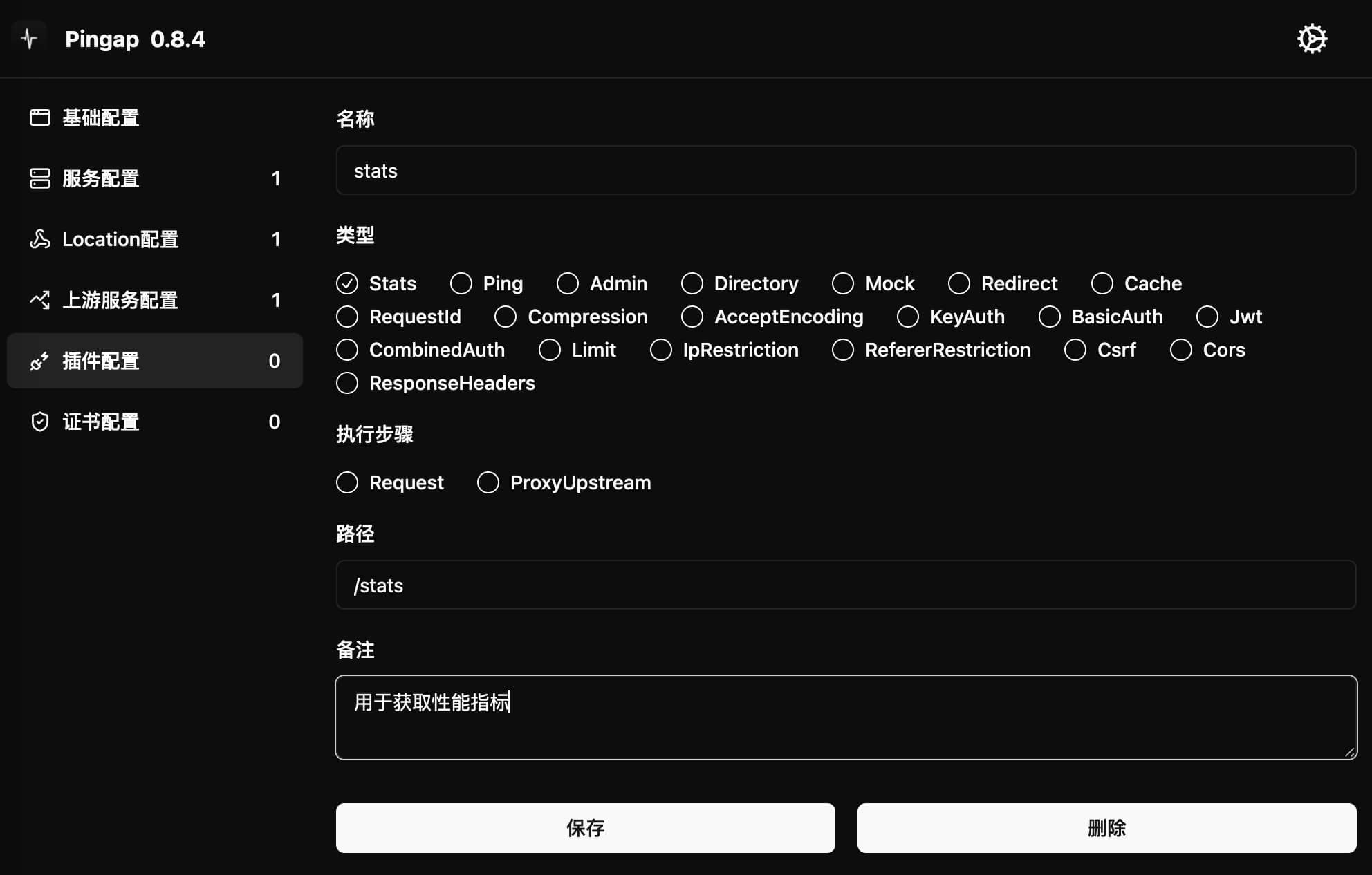
Stats Performance Monitoring Plugin
The Stats plugin exposes application performance metrics for third-party system monitoring. It can be used in two ways:
- Using the built-in
pingap:statsplugin - Custom configuring a new Stats plugin
Configuration Example
[plugins.stats]
category = "stats"
path = "/stats" # Access path
remark = "Performance metrics collection"
Configuration Parameters
path: Metrics data access path, if configured as/statsthen metrics can be accessed via this pathstep: Plugin execution timing, can be eitherrequestorproxy_upstream
Usage
After configuration, performance metrics can be accessed by visiting the /stats path under the corresponding location.
Ping
The Ping plugin provides a simple health check endpoint for monitoring whether the service is running normally. When reverse proxy is configured, it can also serve as pingap's health check mechanism.
[plugins.pingpong]
category = "ping"
path = "/ping" # Health check path
Configuration Parameters
path: Health check access path, returns "pong" response when accessedstep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequestphase
Usage
After configuration, visiting the configured path (e.g., /ping) will return a "pong" response to verify service availability.
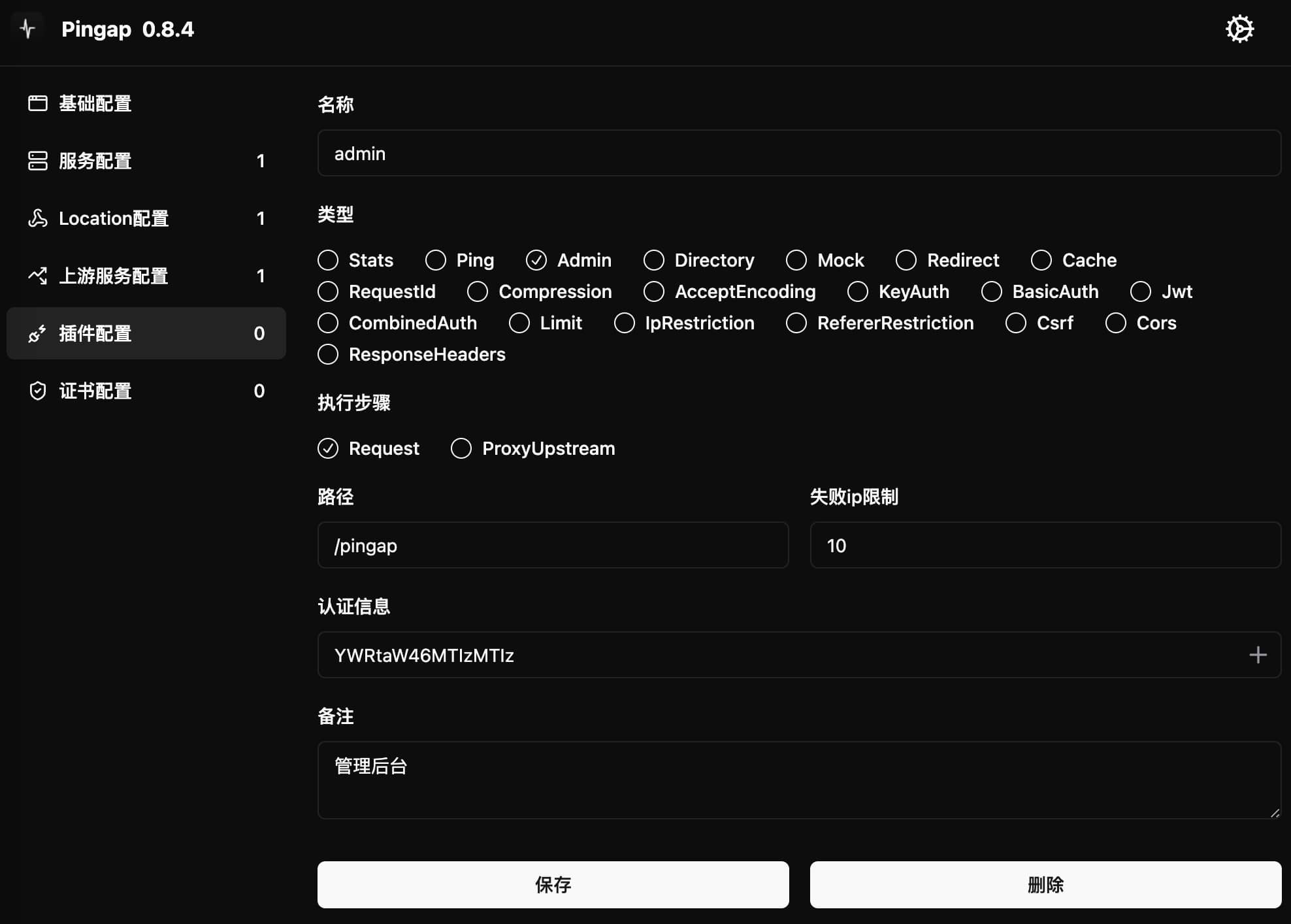
Admin
The Admin plugin adds management backend functionality to existing locations. Configuration example:
[plugins.admin]
authorizations = ["YWRtaW46MTIzMTIz"] # base64(admin:123123)
category = "admin"
ip_fail_limit = 10
max_age = "7d"
path = "/pingap"
remark = "Management backend"
Configuration Parameters
authorizations: List of Basic authentication keys, using base64 encodedusername:passwordformatip_fail_limit: Maximum number of authentication failures allowed per IPpath: Management backend access pathmax_age: Login session validity period, defaults to 2 daysstep: Plugin execution timing, can be eitherrequestorproxy_upstream
Usage
- Associate plugin configuration with specified location
- Access the configured path (e.g.,
/pingap/) to enter management backend - Login using configured credentials (in example:
admin/123123)
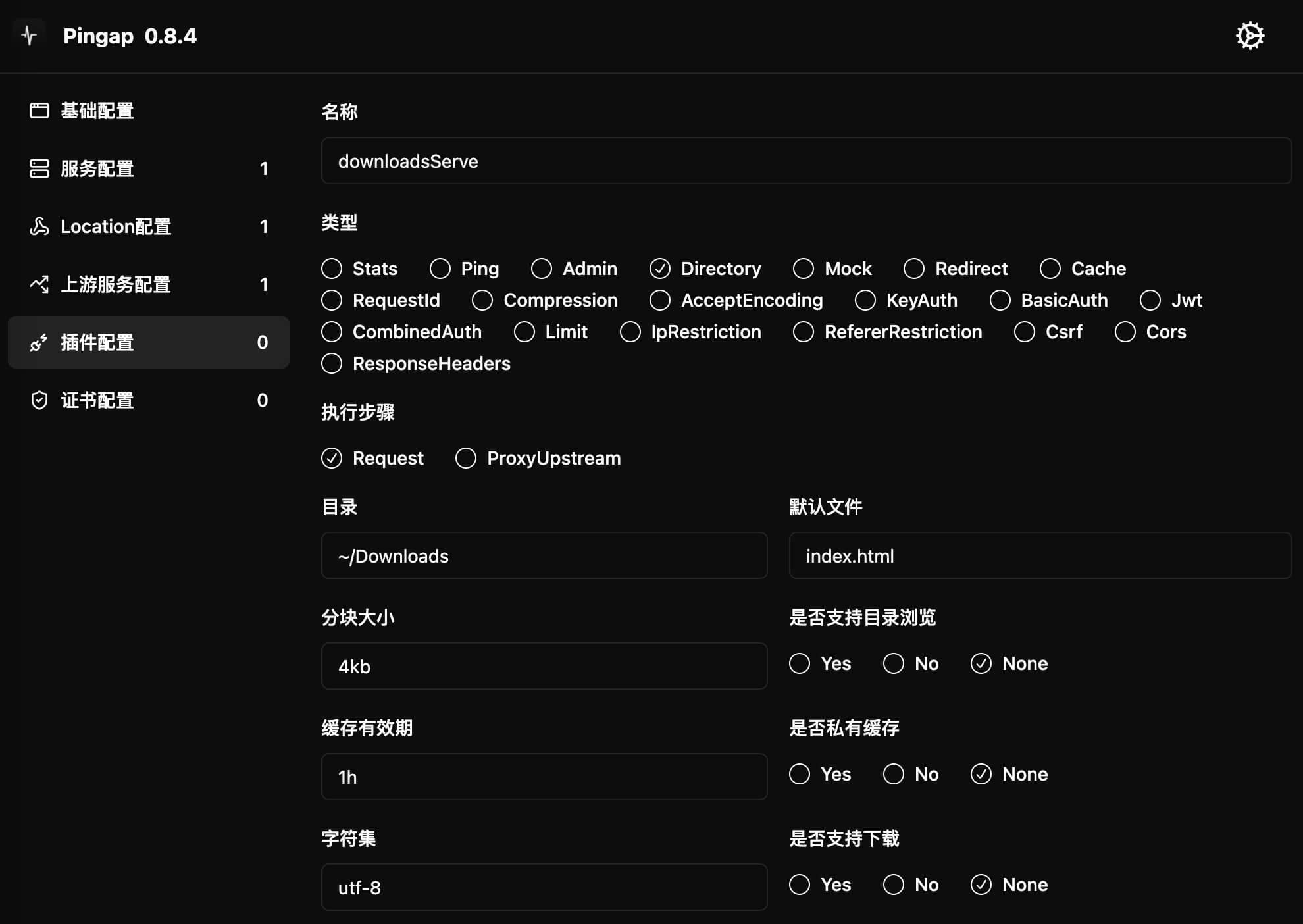
Directory
The Directory plugin provides static file serving functionality, supporting file browsing and downloads.
Configuration Example
[plugins.downloadsServe]
category = "directory"
path = "~/Downloads"
chunk_size = "4kb"
max_age = "1h"
private = true
index = "index.html"
charset = "utf-8"
autoindex = true
download = true
headers = [
"X-Server:pingap",
]
Configuration Parameters
path: Static file directory pathchunk_size: HTTP chunked transfer size, default8kbmax_age: HTTP cache time- No cache by default
- Cache always disabled for
text/htmltype - e.g.,
1hmeans cache for 1 hour
private: Whether to set cache asprivate(default ispublic)index: Default index filename, defaults toindex.htmlcharset: Specify character encoding, not set by defaultautoindex: Whether to enable directory browsing- When enabled,
indexparameter will be ineffective
- When enabled,
download: Whether to enable file downloads- When enabled, sets
Content-Dispositionresponse header
- When enabled, sets
headers: Custom HTTP response header liststep: Plugin execution timing, can be eitherrequestorproxy_upstream
Usage
Configure static file directory path in interface and adjust other parameters as needed:
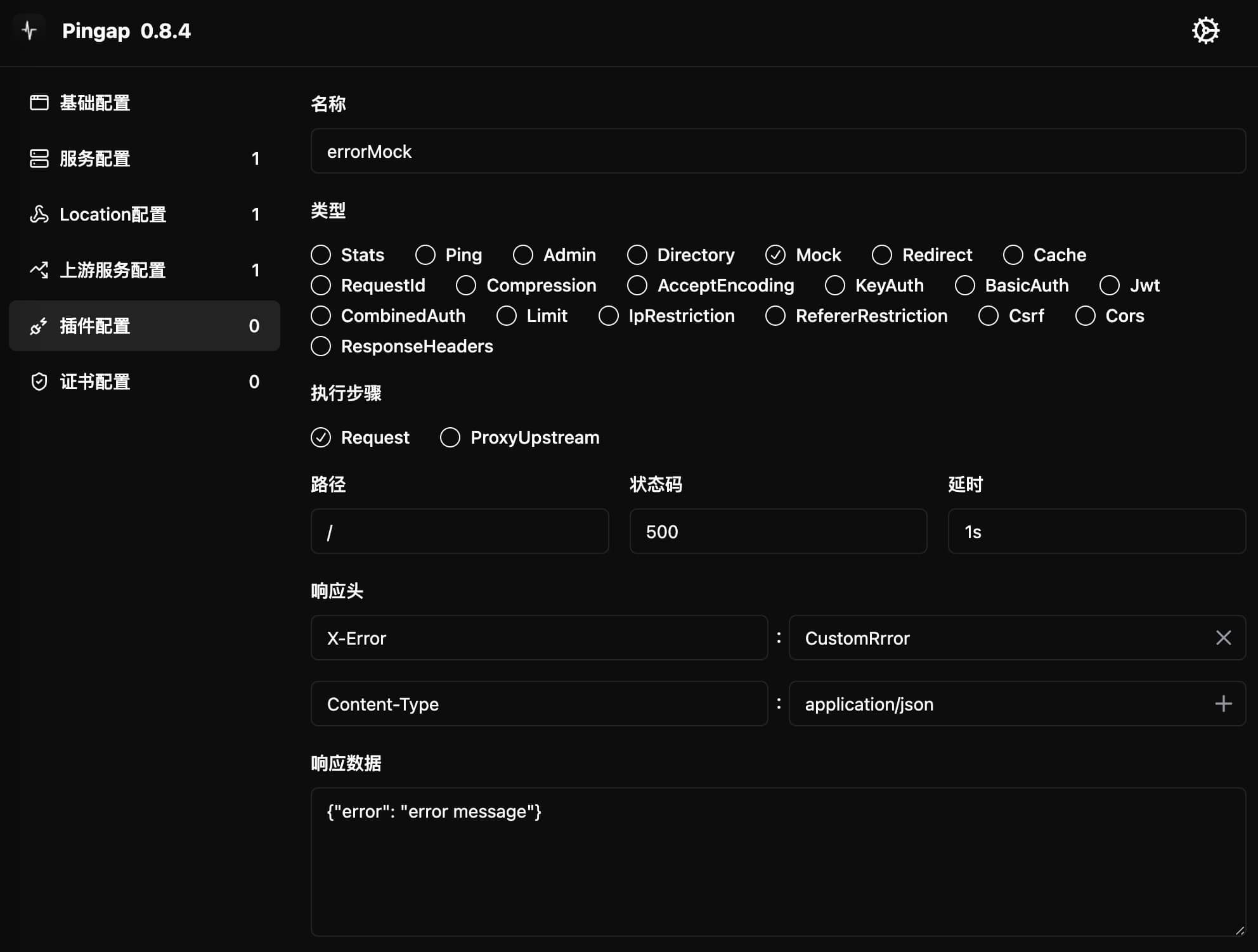
Mock
The Mock plugin is used to simulate HTTP responses, useful for testing or temporary service degradation. Supports customizing response content, status codes, and response headers.
Configuration Example
[plugins.errorMock]
category = "mock"
data = '{"error": "error message"}'
delay = "1s"
headers = [
"X-Error:CustomError",
"Content-Type:application/json",
]
path = "/"
status = 500
step = "request"
Configuration Parameters
data: Simulated response data- For different data types, corresponding
Content-Typeneeds to be specified inheaders
- For different data types, corresponding
headers: Custom response header listpath: Request path that needs response simulation- If not configured, matches all paths
status: HTTP response status codedelay: Response delay timestep: Plugin execution timing, can be eitherrequestorproxy_upstream
Usage
Configure response data and related parameters in the interface, ensuring correct Content-Type is set according to response data type:
Redirect
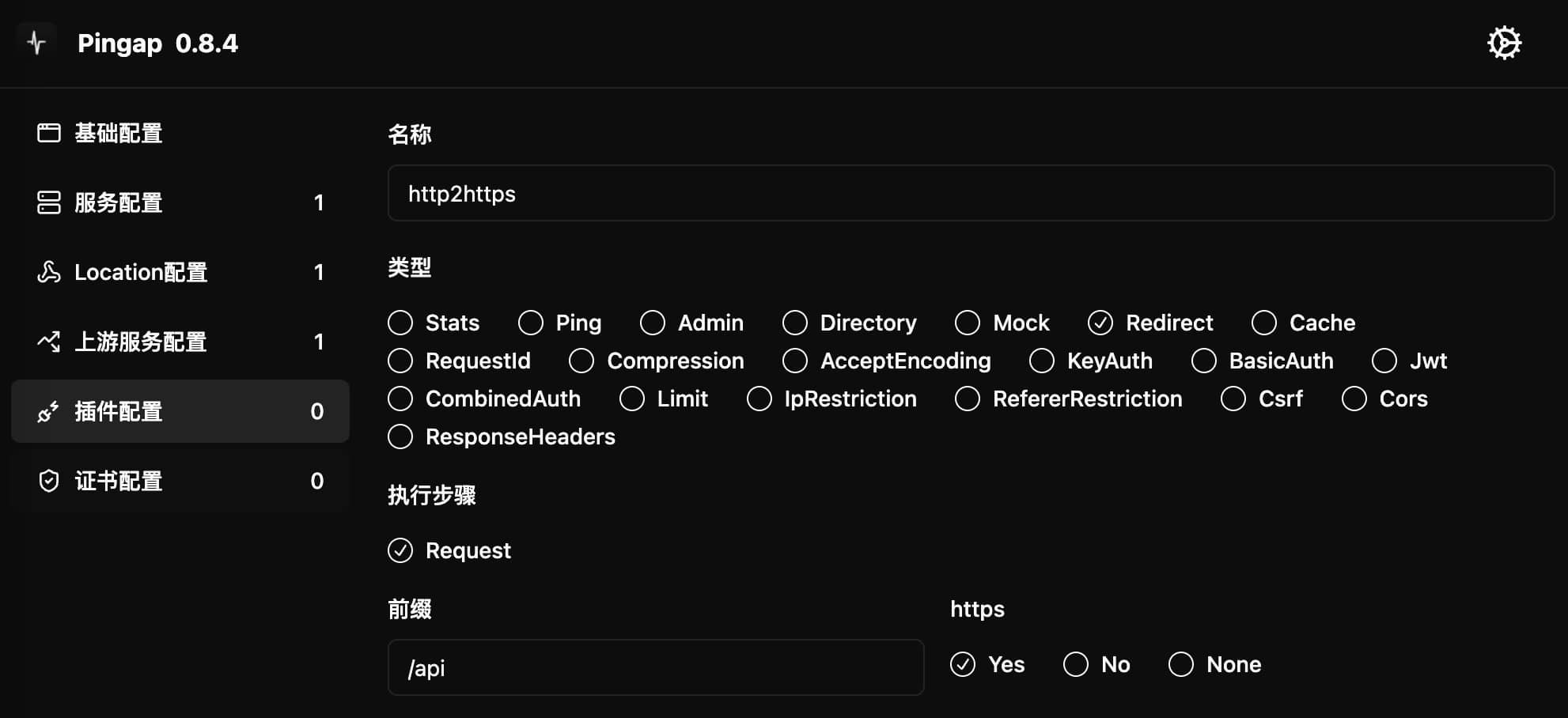
The Redirect plugin is used for HTTP request redirection, supporting URL prefix addition or redirecting HTTP requests to HTTPS.
Configuration Example
[plugins.http2https]
category = "redirect"
http_to_https = true
prefix = "/api"
step = "request"
Configuration Parameters
http_to_https: Whether to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPSprefix: URL prefix to add during redirectionstep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Usage
Configure redirection parameters in the interface:
- Enable HTTPS redirection: check
http_to_https - Add URL prefix: fill in the
prefixfield (optional)
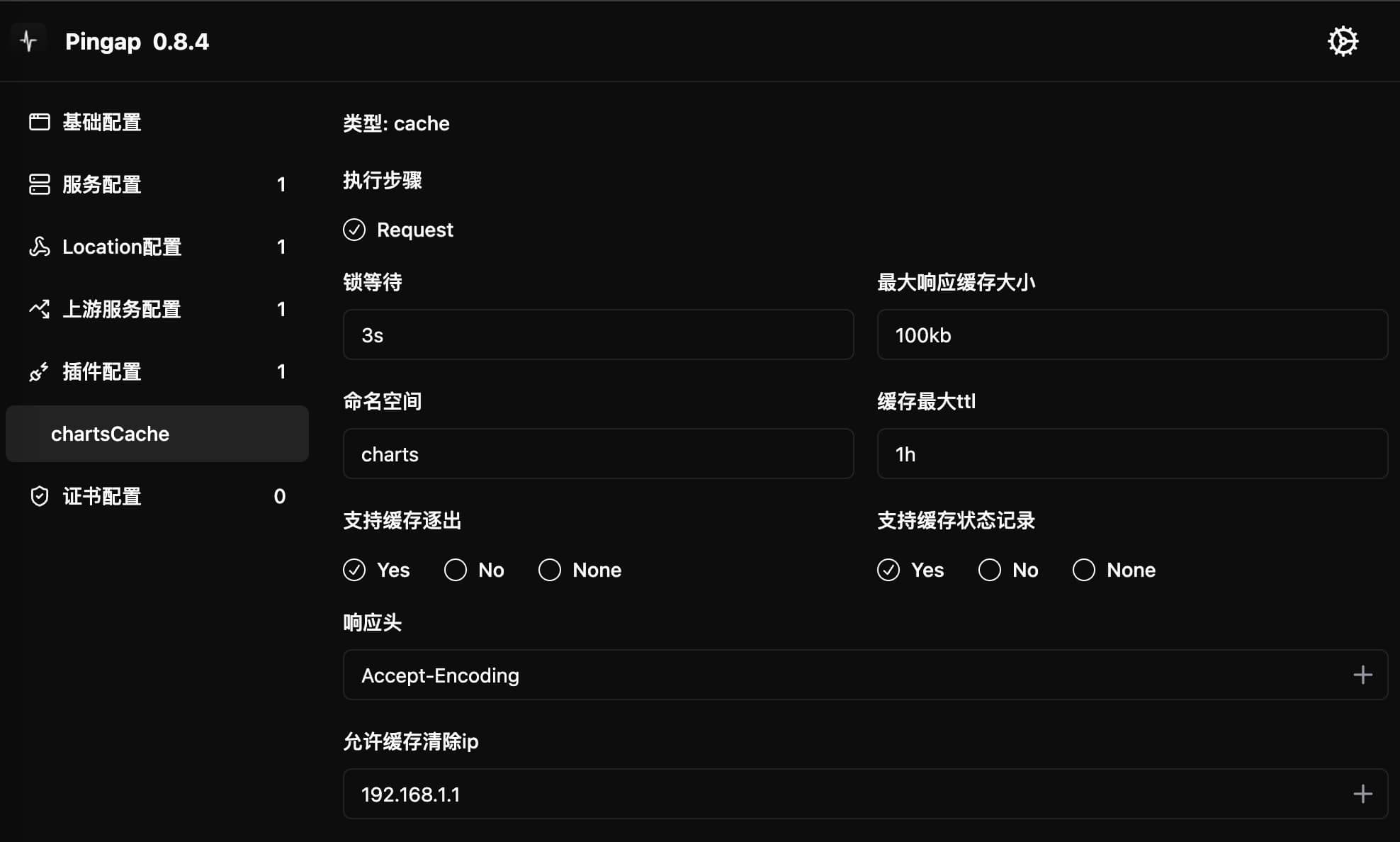
Cache
Cache middleware for HTTP request caching. Since the cache module is used globally, to avoid conflicts with same URLs, it's recommended that each location uses different plugins and sets different namespaces.
Configuration Example
[plugins.chartsCache]
category = "cache"
eviction = true
headers = ["Accept-Encoding"]
lock = "3s"
max_file_size = "100kb"
max_ttl = "1h"
namespace = "charts"
predictor = true
purge_ip_list = [
"127.0.0.1",
"192.168.1.1/24"
]
Configuration Parameters
lock: Wait time for same requests when cache doesn't exist, default 1 second- Used to avoid cache penetration
max_file_size: Maximum size for single cache file, default 1MB- Recommend setting reasonable value to avoid large responses consuming too much memory
namespace: Cache namespace- Cache key generated based on path + querystring
- Recommend using different namespaces for multi-domain scenarios
- Corresponds to separate directory for file caching
max_ttl: Maximum cache validity period- When upstream response's
Cache-Controlmax-ageis long, recommend setting shorters-maxage - When upstream hasn't set
s-maxage, can limit cache time through this config
- When upstream response's
eviction: Whether to enable cache eviction mechanism- Triggers eviction when cache exceeds limit
- File cache automatically cleans long-unused cache, can be left unset
predictor: Whether to record uncacheable requests- Avoids repeated determination of request cacheability
headers: Request header list to be part of cache key- Configure when response depends on certain request headers
- Example: include
Accept-Encodingwhen upstream supports different compression algorithms
purge_ip_list: IP list allowed to execute purge requests, empty by defaultskip: Regular expression to skip caching, empty by default- Used to quickly skip cache determination for certain requests
step: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Interface Configuration
RequestId
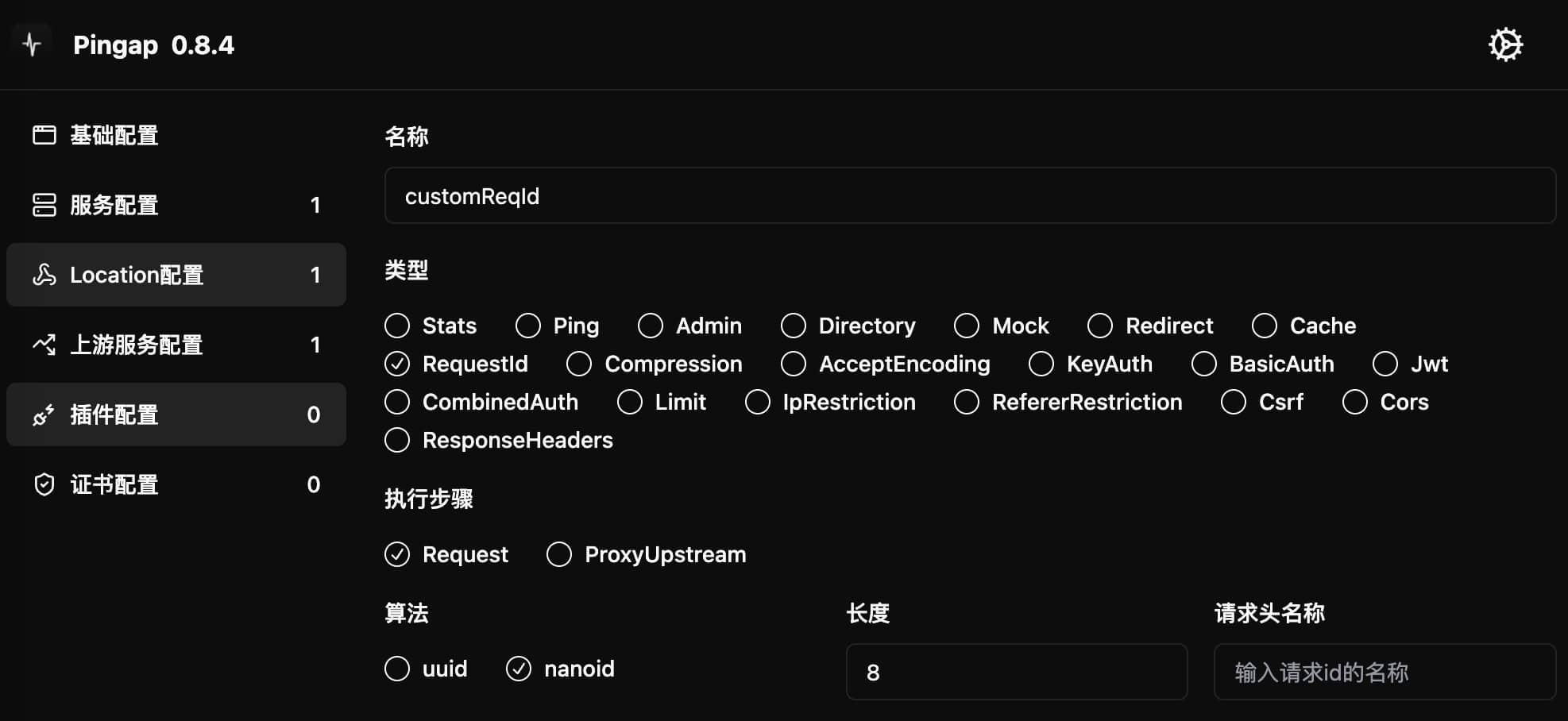
Adds a unique identifier for each request. By default, added to the X-Request-Id request header (header name can be customized). If the request header already exists, the original value is preserved.
Configuration Example
[plugins.customReqId]
algorithm = "nanoid" # Options: uuid or nanoid
category = "request_id"
size = 8 # nanoid length, only effective when algorithm=nanoid
header = "X-Request-Id" # Optional: custom header name
step = "request" # Optional: request or proxy_upstream
Configuration Parameters
algorithm: Algorithm for generating request IDuuid: Uses UUID v4 formatnanoid: Uses NanoID format (shorter, URL safe)
size: NanoID length, only effective when algorithm=nanoidheader: Custom request header name, defaults toX-Request-Idstep: Plugin execution timing, can be eitherrequestorproxy_upstream
Use Cases
- Request tracing: Facilitates request path tracing in distributed systems
- Log correlation: Correlates logs from different services using request ID
- Problem troubleshooting: Quickly locate issues using request ID
Compression
HTTP response compression plugin for handling upstream return data compression. Supports three compression algorithms: gzip, brotli(br), and zstd.
Working Principle
Since Pingora's default compression algorithm matching order is gzip --> br --> zstd, and modern browsers' support for these algorithms is:
- gzip: Almost universally supported
- br(brotli): Mostly supported
- zstd: Partially supported
To optimize compression effect, this plugin adjusts the Accept-Encoding header to prioritize algorithms as zstd --> br --> gzip.
Configuration Example
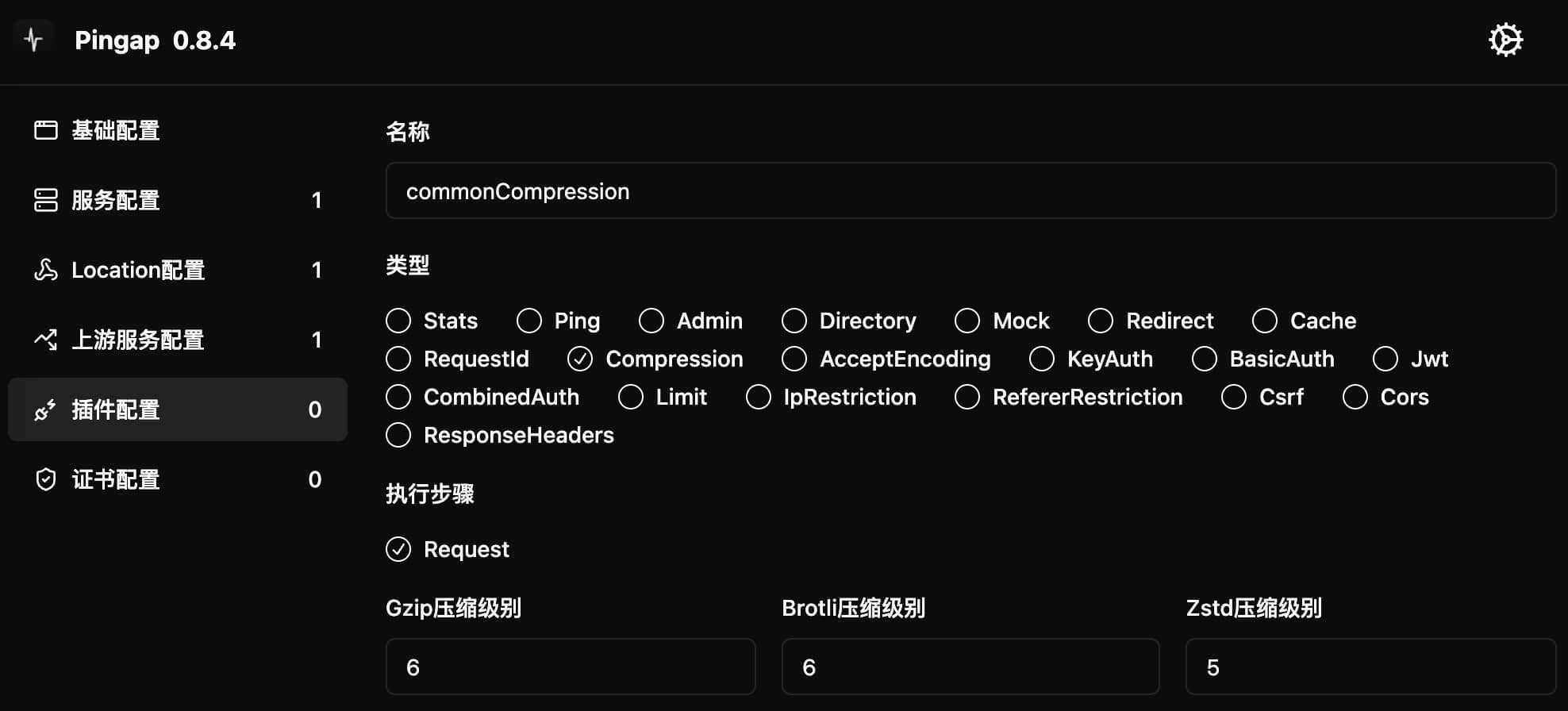
[plugins.commonCompression]
category = "compression"
br_level = 6 # brotli compression level (0-11)
gzip_level = 6 # gzip compression level (0-9)
zstd_level = 5 # zstd compression level (0-22)
decompression = true
Configuration Parameters
br_level: brotli compression level, range 0-11, 0 means disabledgzip_level: gzip compression level, range 0-9, 0 means disabledzstd_level: zstd compression level, range 0-22, 0 means disableddecompression: Whether to decompress upstream returned compressed data
Built-in Configuration
You can use the built-in pingap:compression plugin, which has default configuration:
- gzip_level = 6
- br_level = 6
- zstd_level = 3
Execution Phase
Plugin is fixed to execute in early_request phase, no need to manually specify.
AcceptEncoding
Used to manage and optimize HTTP request's Accept-Encoding header, allowing customization of supported compression algorithms and their priority order.
Configuration Example
[plugins.acceptEncoding]
category = "accept_encoding"
encodings = "zstd, br, gzip" # Supported encodings and priority order
only_one_encoding = true # Whether to use single encoding only
Configuration Parameters
encodings: Specifies supported compression algorithms and their priority order- Multiple algorithms separated by commas
- Order from left to right represents priority from high to low
- Supported algorithms: zstd, br(brotli), gzip
only_one_encoding: Whether to keep only one encoding methodtrue: Only use highest priority supported encodingfalse: Keep all supported encodings, sorted by priority
Execution Phase
Plugin is fixed to execute in early_request phase, no need to manually specify.
KeyAuth
Provides a simple API key authentication mechanism, supporting authentication information retrieval from request parameters (query) or request headers. Can configure multiple valid keys to facilitate multi-system access.
Configuration Example
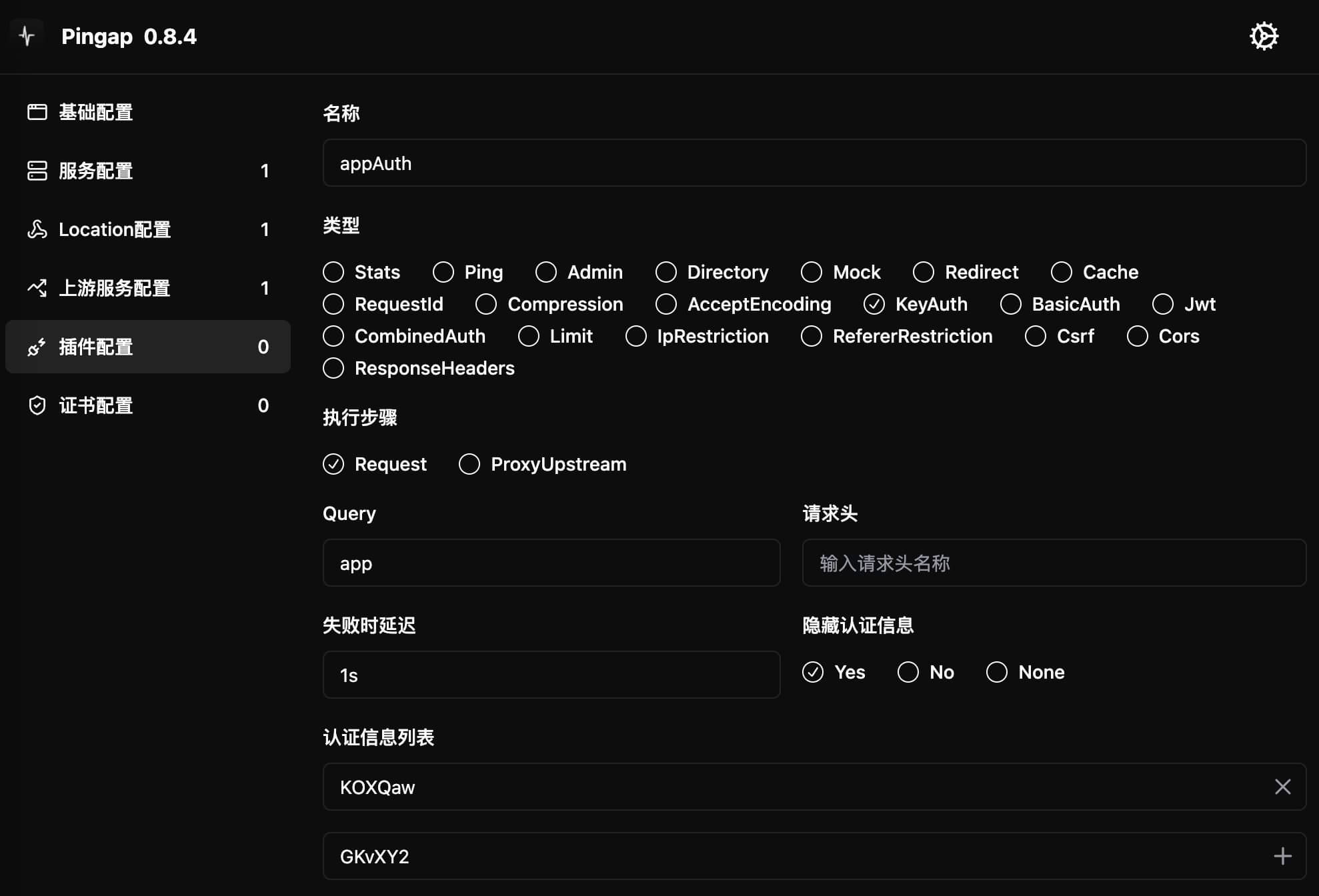
Getting Authentication from Request Parameters
[plugins.queryAuth]
category = "key_auth"
query = "app" # Get key from URL parameter 'app'
keys = [ # List of allowed keys
"KOXQaw",
"GKvXY2",
]
delay = "1s"
hide_credentials = true
step = "request"
Getting Authentication from Request Headers
[plugins.headerAuth]
category = "key_auth"
header = "X-App" # Get key from X-App header
keys = [ # List of allowed keys
"KOXQaw",
"GKvXY2",
]
delay = "1s"
hide_credentials = true
step = "request"
Configuration Parameters
query: Parameter name to get key from request parametersheader: Header name to get key from request headers- Choose either
queryorheader, if both configured,querytakes priority
- Choose either
keys: List of allowed keysdelay: Response delay time for authentication failurehide_credentials: Whether to remove authentication info when forwarding requeststep: Plugin execution timing, can be eitherrequestorproxy_upstream
Interface Configuration
Configure key retrieval method (request parameters or headers) and corresponding valid key list:
BasicAuth
Provides HTTP Basic Authentication functionality. Supports configuring multiple username/password pairs, must be configured in base64 encoded format.
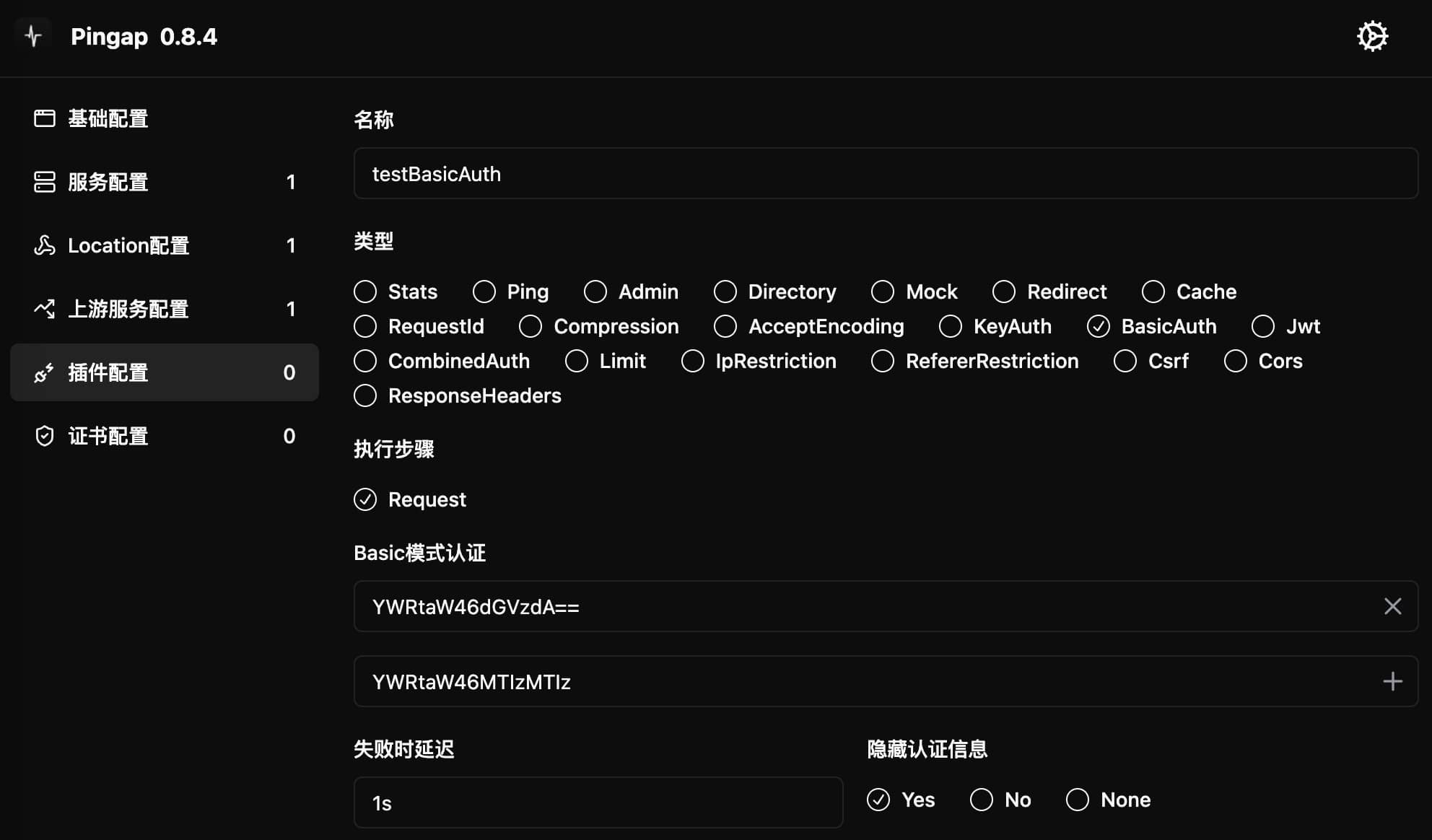
Configuration Example
[plugins.testBasicAuth]
authorizations = [
"YWRtaW46dGVzdA==", # admin:test
"YWRtaW46MTIzMTIz", # admin:123123
]
category = "basic_auth"
delay = "1s"
hide_credentials = true
step = "request"
Configuration Parameters
authorizations: List of authentication credentials- Format is
base64(username:password) - Can configure multiple credentials
- Format is
delay: Response delay time for authentication failurehide_credentials: Whether to remove authentication info when forwarding requeststep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Usage Instructions
- Concatenate username and password in
username:passwordformat - Base64 encode the concatenated result
- Add the encoded string to the
authorizationslist
For example:
admin:test->YWRtaW46dGVzdA==admin:123123->YWRtaW46MTIzMTIz
JWT
Provides JWT (JSON Web Token) authentication functionality. Includes two main functions:
- Generate JWT token at specified path
- Verify if JWT token carried in request is valid
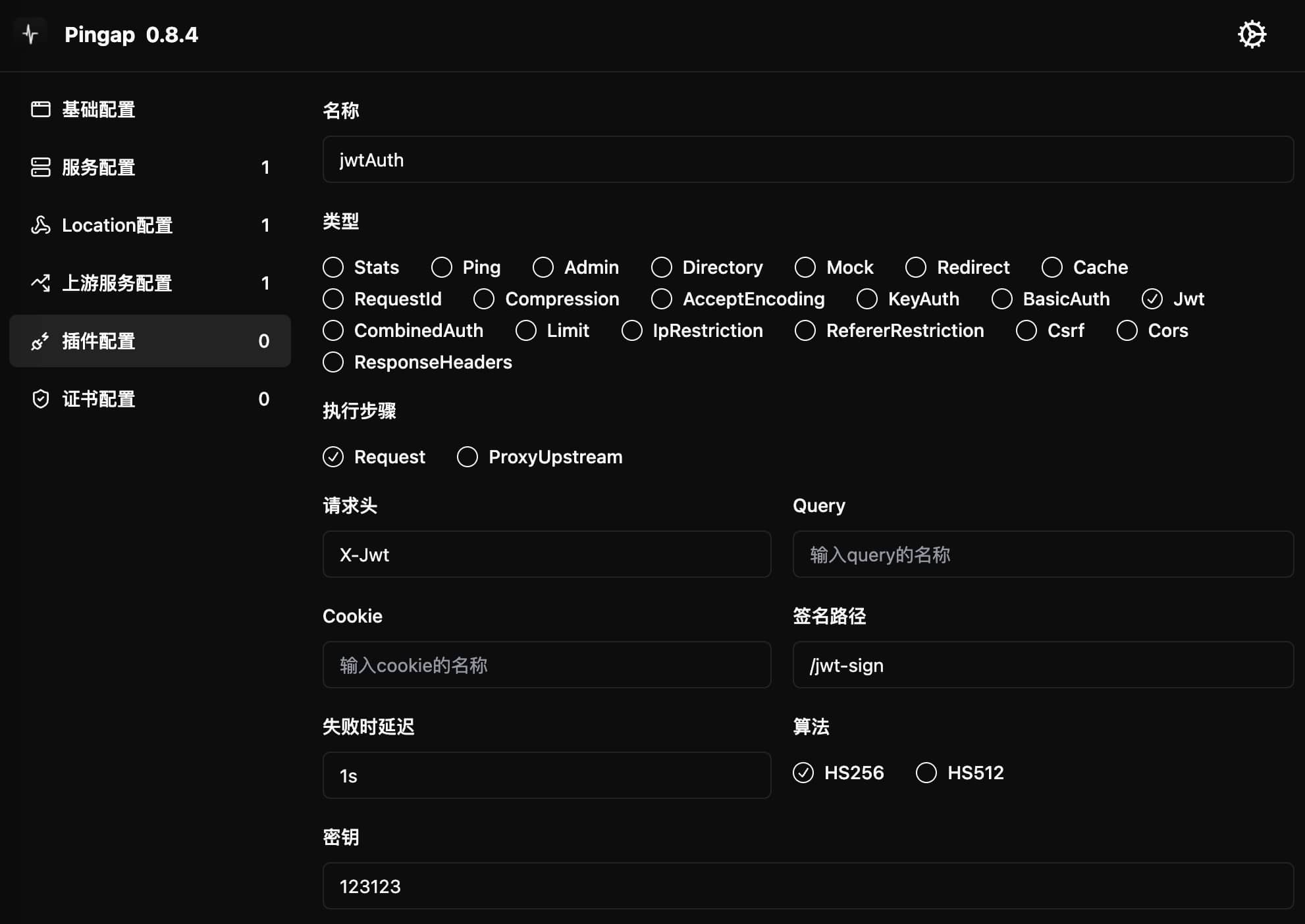
Configuration Example
[plugins.jwtAuth]
algorithm = "HS256"
auth_path = "/jwt-sign"
category = "jwt"
delay = "1s"
header = "X-Jwt"
secret = "123123"
step = "request"
Configuration Parameters
auth_path: Path used to generate JWT token- When accessing this path, response data will be used as payload to generate token
algorithm: JWT signing algorithm, currently supports HS256secret: Signing keyheader: Header field name to get token from requestcookie: Cookie field name to get token fromquery: URL parameter name to get token from- Token retrieval priority: header > cookie > query
- At least one of these three parameters must be configured
delay: Response delay time for authentication failurestep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Workflow
-
Generate token:
- Access path configured in
auth_path - Use response data as payload to sign and generate token
- Return generated token
- Access path configured in
-
Verify token:
- When accessing other paths, get token according to priority
- Verify token signature and validity
- Continue processing if verification passes, otherwise return authentication error
CombinedAuth
Provides combination authentication mechanism based on application ID, key, and timestamp. Supports configuring independent authentication parameters and IP whitelist for each application.
Configuration Example
[plugins.appAuth]
category = "combined_auth"
step = "request"
[[plugins.appAuth.authorizations]]
app_id = "pingap"
deviation = 10
ip_list = [
"192.168.1.1/24",
"127.0.0.1",
]
secret = "123123"
Configuration Parameters
app_id: Application identifiersecret: Key used for generating digestdeviation: Allowed timestamp deviation (in seconds)- Used to handle cases where client and server time are not perfectly synchronized
ip_list: IP whitelist allowed to access- Supports single IP and CIDR format networks
step: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Authentication Process
-
Client constructs request parameters:
app_id: Configured application identifierts: Current timestampdigest: Digest value calculated using SHA256 algorithm- Calculation formula:
SHA256(secret:timestamp)
- Calculation formula:
-
Request example:
GET /api?app_id=pingap&ts=1727582506&digest=85c623c389177a69860adfd572212507ef98c197ba5105677919e0663eeae091
- Server verification:
- Check if request IP is in whitelist
- Verify if timestamp is within allowed deviation range
- Calculate digest using same algorithm and compare
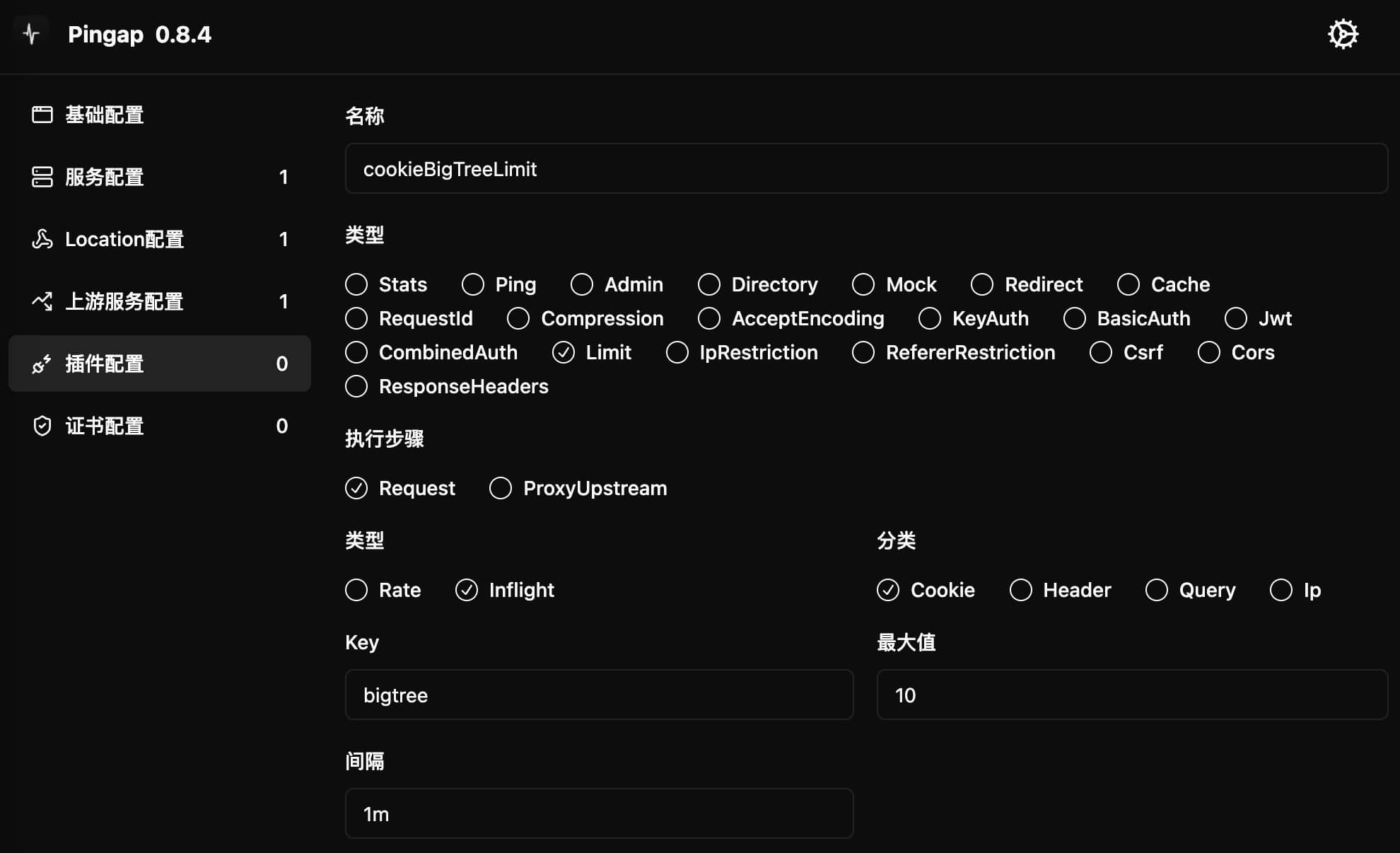
Limit
Provides access restriction functionality based on multiple conditions. Supports two types of limitations: concurrent connections (inflight) and access rate (rate), which can be restricted based on Cookie, request headers, URL parameters, or IP address.
Configuration Parameters
type: Limitation typeinflight: Concurrent access limitrate: Access frequency limit
tag: Restriction condition sourcecookie: Get from Cookieheader: Get from request headerquery: Get from URL parameterip: Based on visitor IP
key: Field name to get limitation value- Not required when using
iptype
- Not required when using
max: Maximum allowed valueinterval: Statistics time interval (only for rate type)step: Plugin execution timing, can be eitherrequestorproxy_upstream
Configuration Examples
- Cookie-based concurrent limit:
[plugins.cookieBigTreeLimit]
category = "limit"
type = "inflight"
tag = "cookie"
key = "bigtree"
max = 10
step = "request"
- Header-based concurrent limit:
[plugins.headerAppLimit]
category = "limit"
type = "inflight"
tag = "header"
key = "X-App"
max = 10
- URL parameter-based rate limit:
[plugins.queryAppLimit]
category = "limit"
type = "rate"
tag = "query"
key = "app"
max = 10
interval = "1s"
- IP-based rate limit:
[plugins.ipLimit]
category = "limit"
type = "rate"
tag = "ip"
max = 10
interval = "1m"
Additional Notes
- IP retrieval priority: X-Forwarded-For > X-Real-Ip > Remote Addr
- No limit applied when restriction condition value is empty
- Rate limit requires
intervalparameter - Concurrent limit does not need
intervalparameter
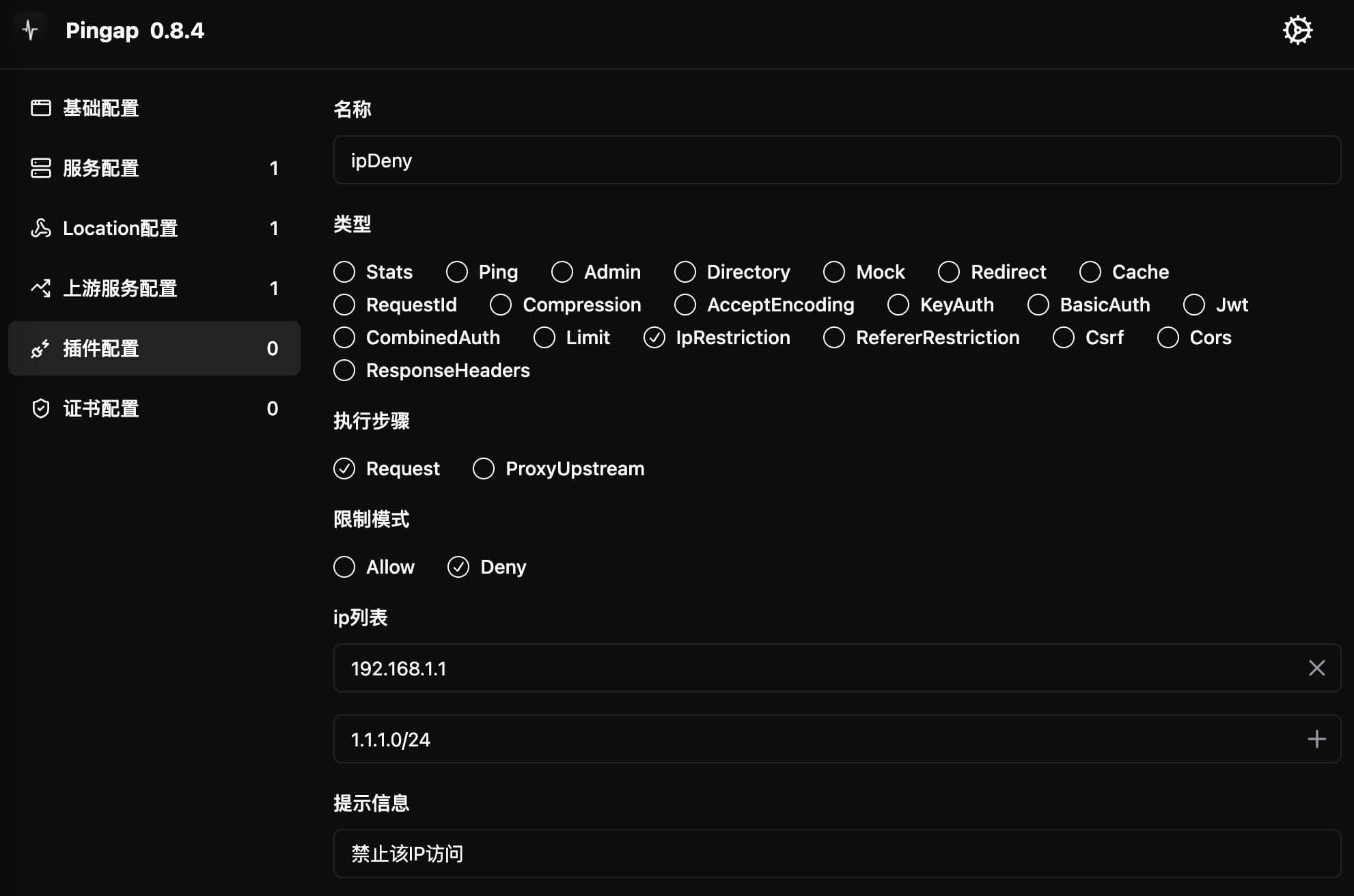
IpRestriction
Provides access control functionality based on IP addresses. Supports setting either allow or deny modes, can configure single IP addresses or CIDR format networks.
Configuration Example
[plugins.ipDeny]
category = "ip_restriction"
ip_list = [
"192.168.1.1", # Single IP address
"1.1.1.0/24", # CIDR format network
]
message = "IP access denied"
step = "request"
type = "deny"
Configuration Parameters
type: Access control modeallow: Only allow IPs in list to accessdeny: Block IPs in list from accessing
ip_list: IP address list- Supports single IP addresses
- Supports CIDR format networks
message: Message shown when access is deniedstep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Usage Instructions
- Select access control mode (allow/deny)
- Add IP addresses or networks that need to be controlled
- Configure message shown when access is denied
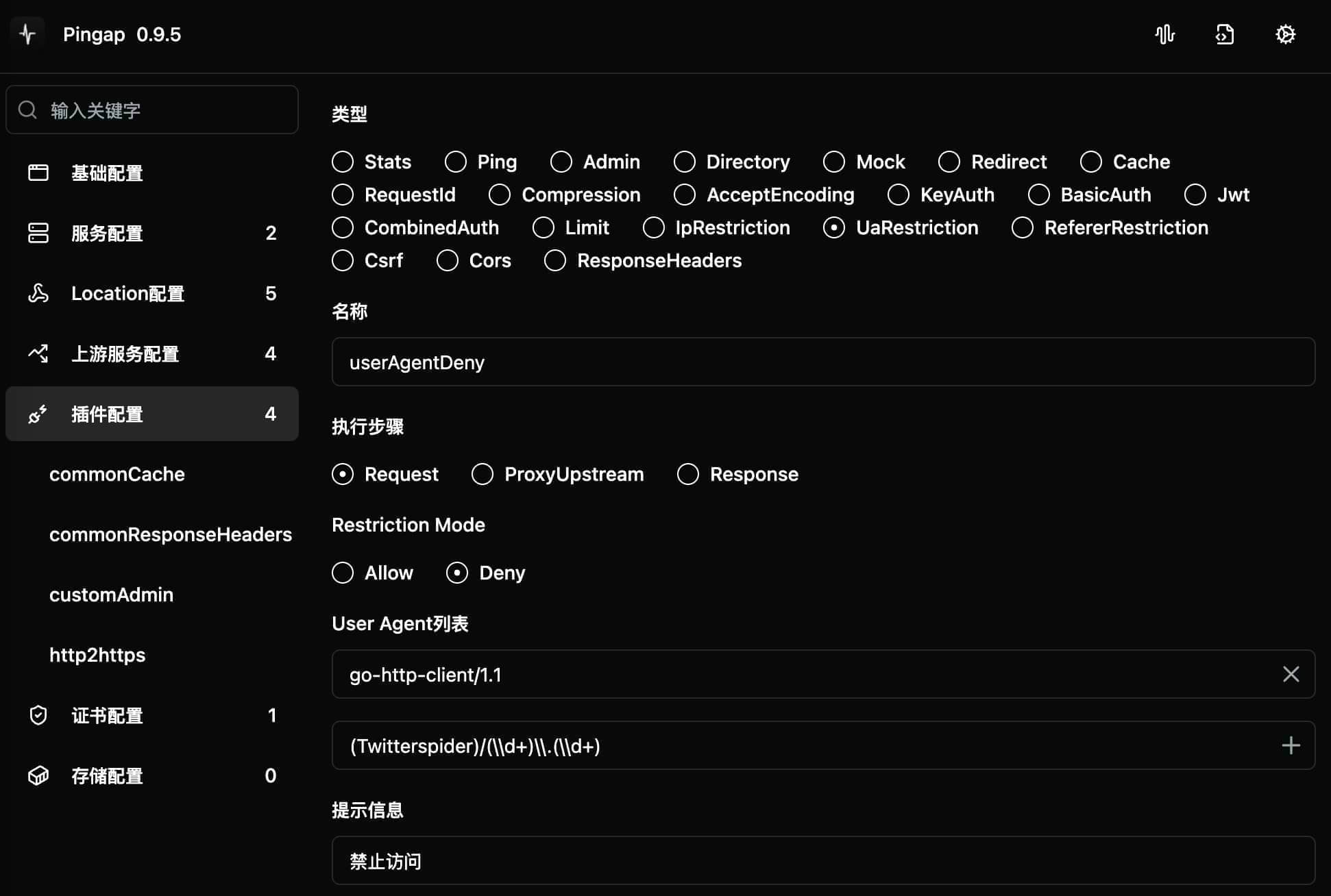
UaRestriction
Provides access control functionality based on User-Agent. Supports setting either allow or deny modes, can use regular expressions for matching.
Configuration Example
[plugins.userAgentDeny]
category = "ua_restriction"
ua_list = [
"go-http-client/1.1", # Exact match
"(Twitterspider)/(\\d+)\\.(\\d+)" # Regex match
]
message = "Access denied"
step = "request"
type = "deny"
Configuration Parameters
type: Access control modeallow: Only allow User-Agents matching listdeny: Block User-Agents matching list
ua_list: User-Agent matching rule list- Supports exact matching
- Supports regular expression matching
message: Message shown when access is deniedstep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Usage Instructions
- Select access control mode (allow/deny)
- Add User-Agent matching rules
- Enter complete User-Agent string for exact matching
- Use regular expressions to match specific patterns
- Configure message shown when access is denied
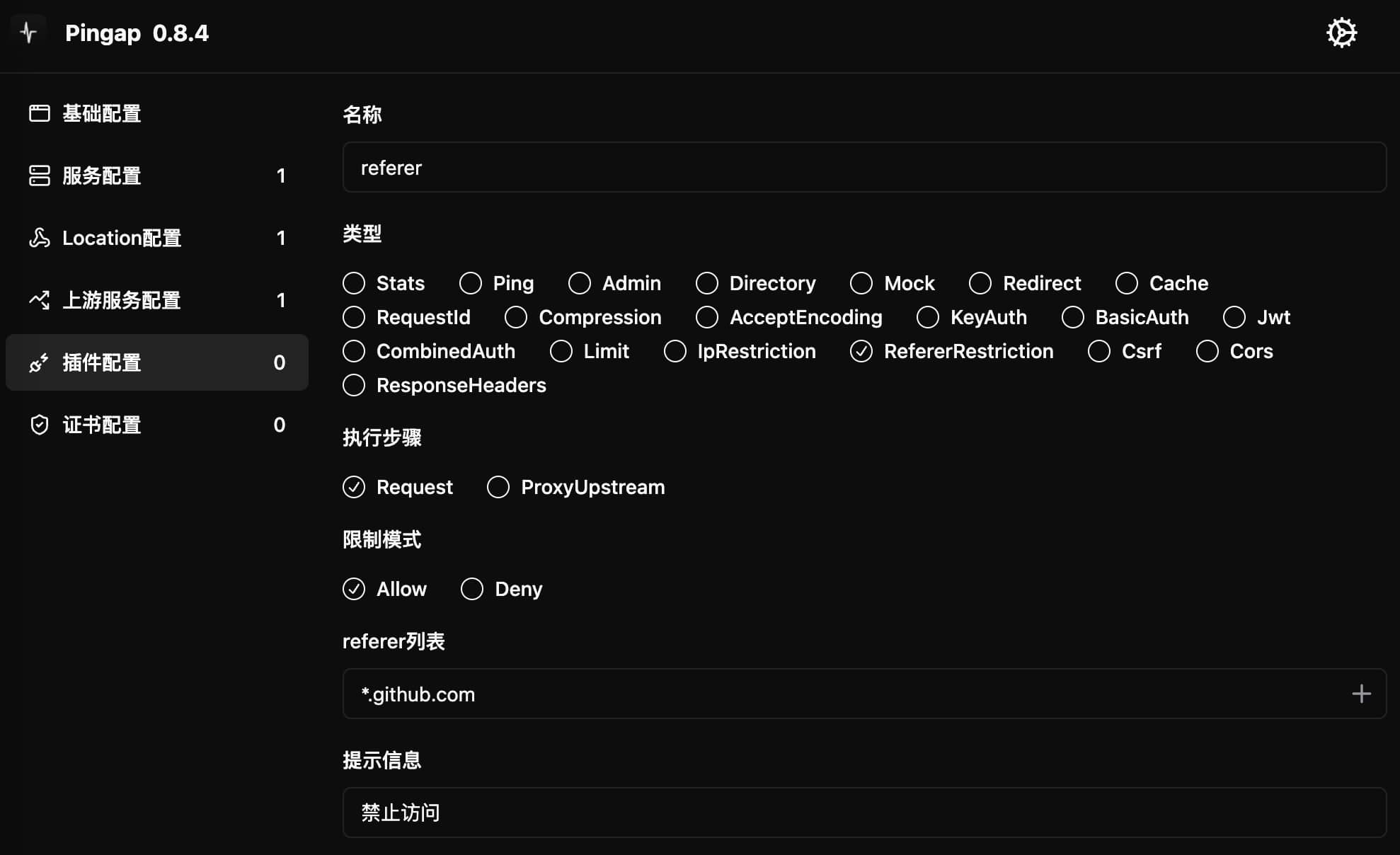
RefererRestriction
Provides access control functionality based on HTTP Referer. Supports setting either allow or deny modes, can use wildcards (*) for domain matching.
Configuration Example
[plugins.referer]
category = "referer_restriction"
referer_list = [
"*.github.com", # Match all github.com subdomains
"example.com" # Exact match
]
message = "Access denied"
step = "request"
type = "allow"
Configuration Parameters
type: Access control modeallow: Only allow Referers matching listdeny: Block Referers matching list
referer_list: Referer matching rule list- Supports exact matching
- Supports using * as wildcard for subdomain matching
message: Message shown when access is deniedstep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Usage Instructions
- Select access control mode (allow/deny)
- Add Referer matching rules
- Enter domain directly for exact matching
- Use
*.domain.comformat to match all subdomains
- Configure message shown when access is denied
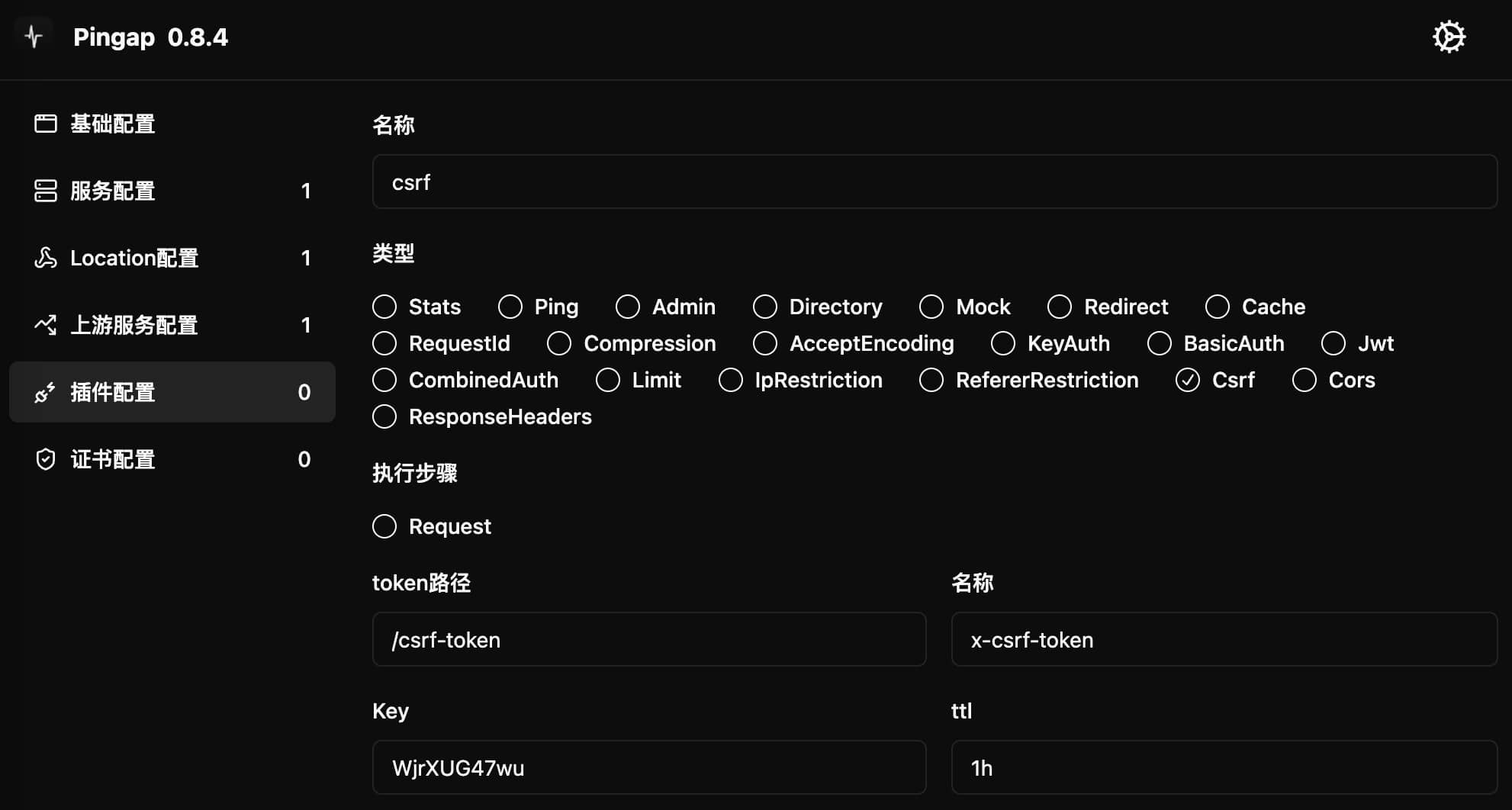
CSRF
Provides Cross-Site Request Forgery protection functionality. Verifies request legitimacy by comparing token values in cookie and request header.
Configuration Example
[plugins.csrf]
category = "csrf"
key = "WjrXUG47wu"
name = "x-csrf-token"
token_path = "/csrf-token"
ttl = "1h"
Configuration Parameters
key: Key used for generating tokenname: CSRF token name- Used as both cookie name and request header name
token_path: Path to get token- New token will be generated when accessing this path
- Sets same-named cookie with SameSite protection enabled
ttl: Token validity periodstep: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Workflow
-
Get token:
- Client accesses path configured in
token_path - Server generates token and sets it in cookie
- Cookie set to SameSite mode for enhanced security
- Client accesses path configured in
-
Request verification:
- Client carries token in request header
- Server compares tokens in request header and cookie
- Request rejected if they don't match
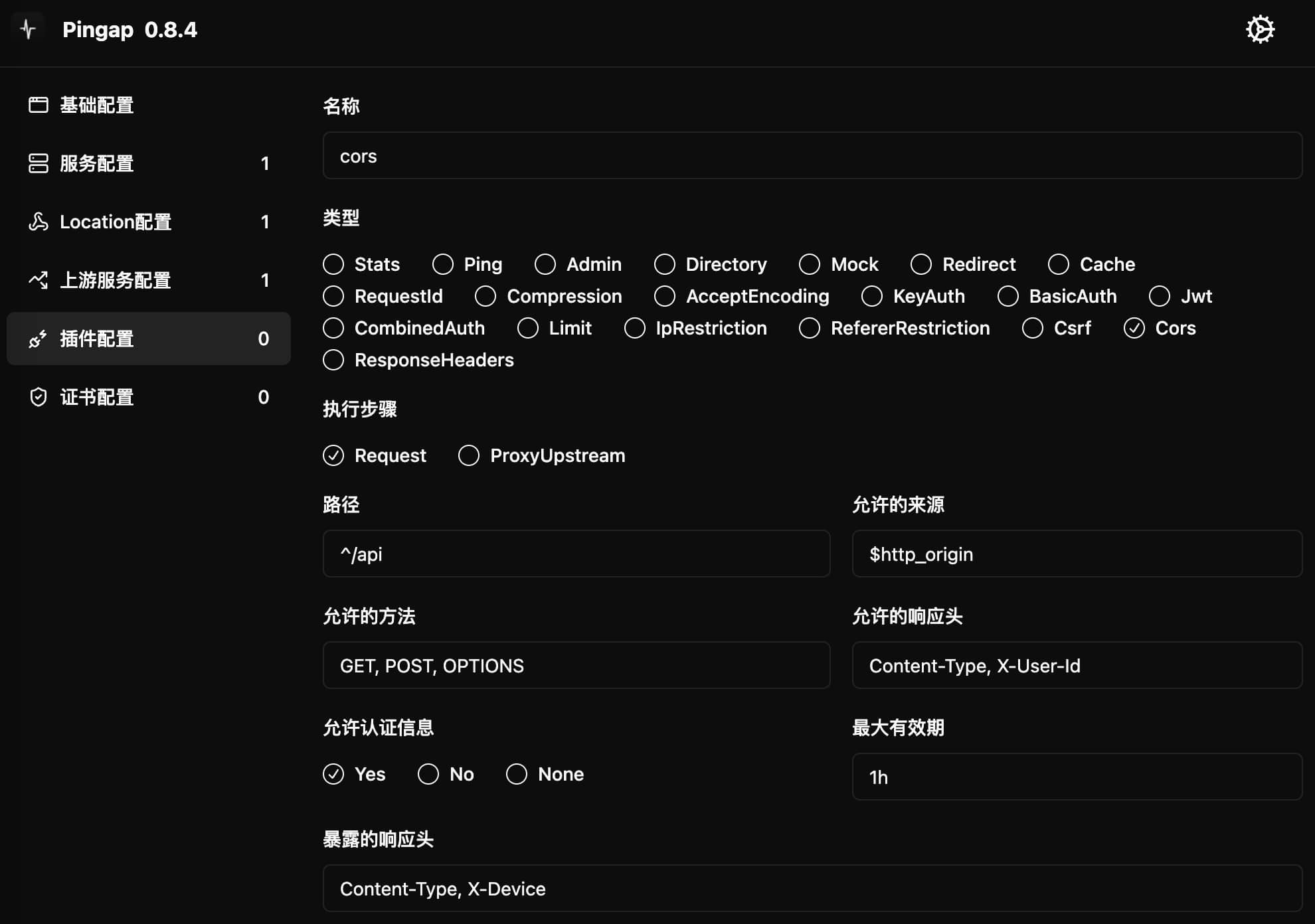
CORS
Provides Cross-Origin Resource Sharing configuration functionality for controlling browser cross-origin access policies.
Configuration Example
[plugins.cors]
allow_credentials = true
allow_headers = "Content-Type, X-User-Id"
allow_methods = "GET, POST, OPTIONS"
allow_origin = "$http_origin"
category = "cors"
expose_headers = "Content-Type, X-Device"
max_age = "1h"
path = "^/api"
step = "request"
Configuration Parameters
allow_origin: Allowed cross-origin request sources- Can specify specific domain like
https://example.com - Set to
$http_originto allow request origin, not recommended for production - Recommend explicitly specifying allowed domain list
- Can specify specific domain like
allow_credentials: Whether to allow carrying authentication information- Includes Cookie, HTTP authentication and client SSL certificates
allow_methods: Allowed HTTP request methods- Multiple methods separated by commas, like
GET, POST, OPTIONS
- Multiple methods separated by commas, like
allow_headers: Allowed custom request headers- Multiple headers separated by commas
expose_headers: Response headers browser is allowed to access- Browsers can only access basic response headers by default
- Can expose custom response headers through this parameter
max_age: Cache time for preflight request resultspath: CORS configuration effective path range- Supports regular expression matching
step: Plugin execution timing, only supportsrequest
Security Recommendations
- Avoid using
$http_origin, explicitly specify allowed domains - Only configure necessary request methods and headers
- Be cautious with
allow_credentials, may bring security risks - Set reasonable
max_ageto balance performance and security
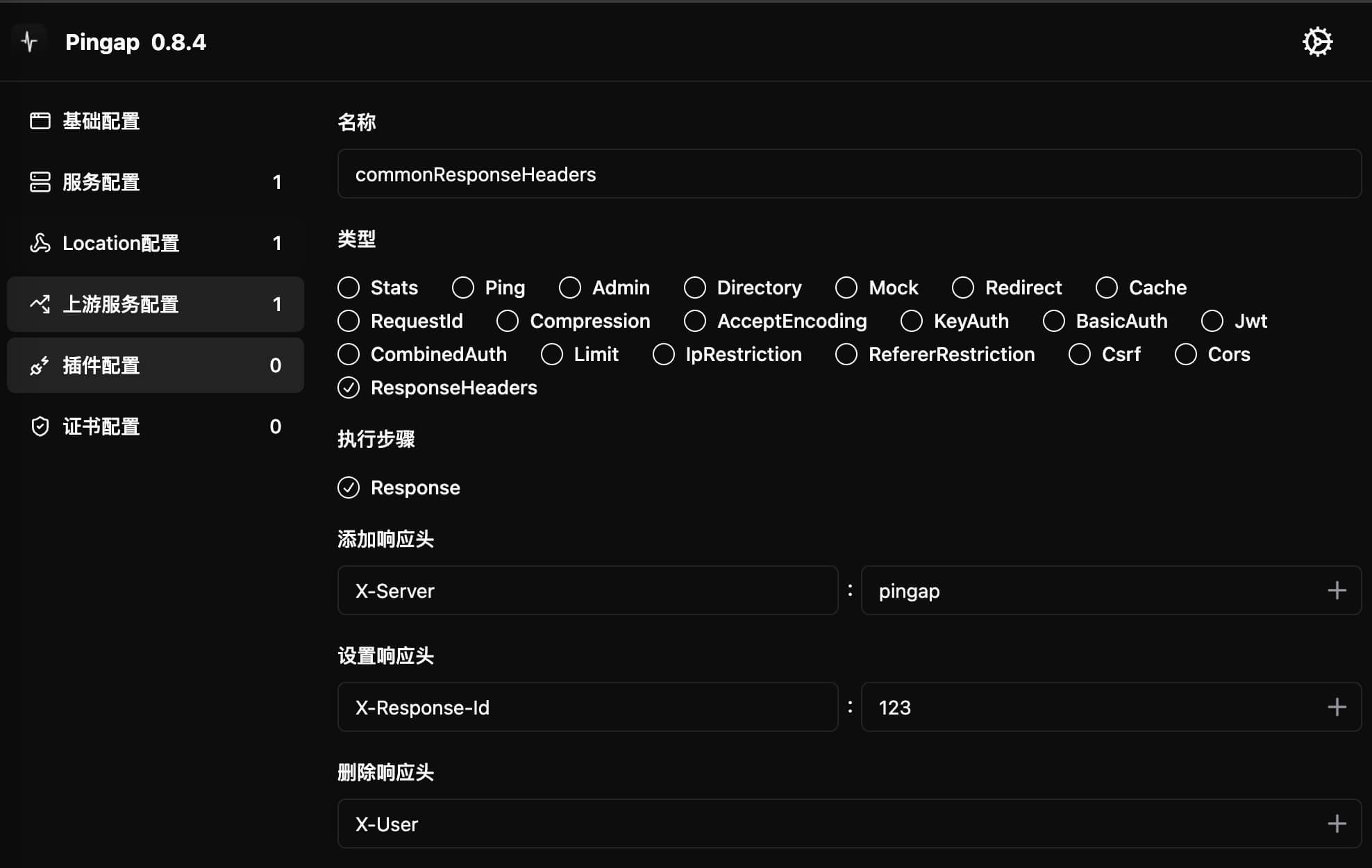
ResponseHeaders
Provides HTTP response header management functionality, supporting adding, setting, and removing response headers. Supports using variable references:
$hostname: Reference server hostname$variable_name: Reference environment variable value
Configuration Example
[plugins.commonResponseHeaders]
add_headers = ["X-Server:pingap"]
category = "response_headers"
remove_headers = ["X-User"]
set_headers = ["X-Response-Id:123"]
step = "response"
Configuration Parameters
add_headers: Response headers to add- Won't override existing headers with same name
set_headers: Response headers to set- Will override existing headers with same name
remove_headers: Response headers to remove- Removes headers with specified names
step: Plugin execution timing, only supportsresponse
Execution Order
Operations execute in following order:
add_headers: Add new response headersremove_headers: Remove specified response headersset_headers: Set (override) response headers
Usage Instructions
- Configure headers to add, set, or remove as needed
- Each configuration item is optional, can omit if not needed
- Header values can use variables:
$hostnamegets server hostname$VARIABLE_NAMEgets environment variable value